Plant-based protein refers to protein sources that are derived primarily from plants, such as legumes, grains, nuts, and seeds, rather than animal sources like meat, dairy, and eggs.
Understanding plant-based protein sources

Plant-based protein sources include legumes, grains, nuts, and seeds. These options are rich in essential nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Legumes, such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas, are excellent sources of protein and can be used in various dishes like soups, salads, and stews. Grains like quinoa and rice also provide protein and can be used as a base for hearty meals. Nuts and seeds, like almonds, chia seeds, and hemp seeds, can be sprinkled on top of salads or blended into smoothies for an extra protein boost.
Benefits of incorporating plant-based protein in your diet
Incorporating plant-based protein into your diet offers numerous benefits. Firstly, it can help improve overall health by providing essential nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Secondly, plant-based protein sources are typically low in saturated fat, making them heart-healthy options. Thirdly, they can aid in weight management as they are often lower in calories compared to animal protein sources. Lastly, plant-based proteins are more environmentally sustainable and ethical, as they have a lower carbon footprint and do not involve animal cruelty.
Different Types of Plant-Based Protein
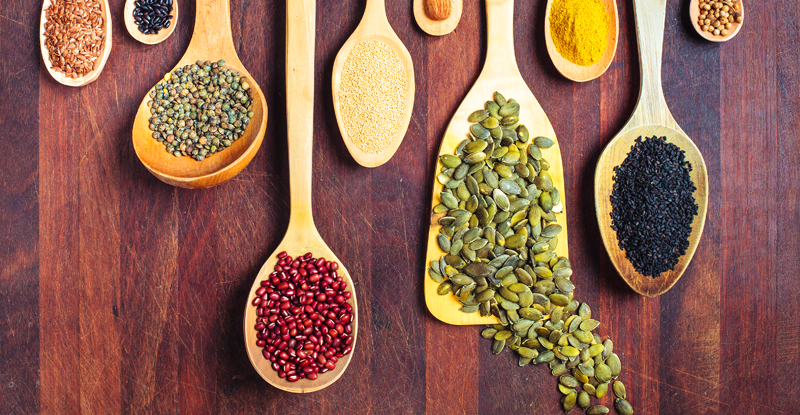

Different Types of Plant-Based Protein
There are various types of plant-based protein sources that you can incorporate into your diet. Some popular options include soy-based proteins, which are versatile and contain all the essential amino acids. Pea protein is another excellent choice, as it is allergen-friendly and easily digestible. Other plant-based protein sources include lentils, chickpeas, quinoa, and nuts. Experimenting with different types of plant-based protein can help diversify your nutrient intake and add variety to your meals. Plus, plant-based proteins are often more sustainable and ethical compared to animal-based proteins.
Soy-based proteins

Soy-based proteins are a versatile and nutritious plant-based protein option that contain all the essential amino acids. You can incorporate soy-based proteins into your diet by using soy milk, tofu, tempeh, or edamame. Experiment with recipes and try making soy-based burgers, stir-fries, or smoothies to add variety and protein to your meals. Soy-based proteins are also a great source of calcium and iron, making them a beneficial choice for overall health and well-being.
Pea protein and its benefits
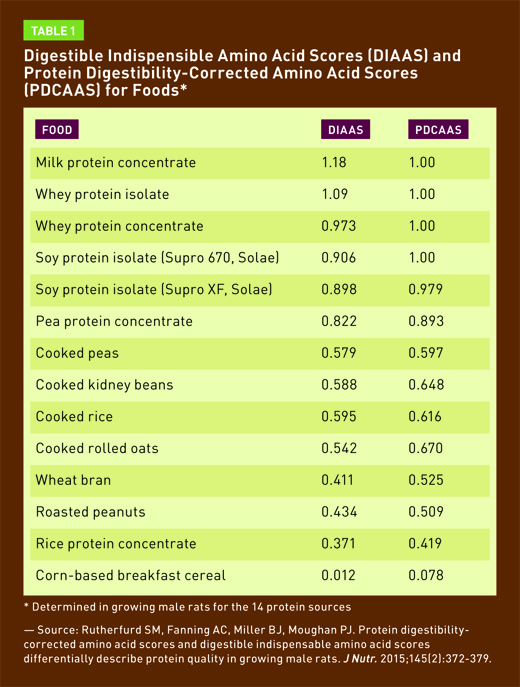
Pea protein and its benefits
Pea protein is a popular plant-based protein option that is derived from yellow peas, offering a range of benefits. It is highly digestible, making it suitable for individuals with digestive sensitivities. Additionally, pea protein is rich in essential amino acids, including lysine and arginine, which play a crucial role in muscle growth and repair. It is also low in allergens, making it an excellent choice for those with dietary restrictions. Incorporating pea protein into your diet can help support muscle recovery, improve satiety, and promote overall health and wellness.
How to Incorporate Plant-Based Protein into Your Diet
- Start your day with a plant-based protein smoothie, using ingredients like almond milk, spinach, and a scoop of plant-based protein powder.
- Substitute meat with plant-based protein alternatives, such as tofu, tempeh, or seitan, in your favorite recipes like stir-fries, tacos, or burgers.
- Snack on roasted chickpeas, edamame, or mixed nuts for a protein-packed pick-me-up during the day.
- Add plant-based protein sources like quinoa, lentils, or beans to your salads, soups, or grain bowls.
- Incorporate plant-based protein snacks, like protein bars or protein balls, into your meal planning for a convenient and on-the-go option.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to ensure you meet your specific nutritional needs when incorporating plant-based protein into your diet.
Plant-based protein meal ideas
Some plant-based protein meal ideas include a protein-packed smoothie made with almond milk, spinach, and plant-based protein powder, substituting meat with tofu, tempeh, or seitan in recipes like stir-fries, tacos, or burgers, snacking on roasted chickpeas, edamame, or mixed nuts, adding quinoa, lentils, or beans to salads, soups, or grain bowls, and incorporating plant-based protein snacks like protein bars or protein balls into your meal planning for convenience and on-the-go options.
Tips for cooking with plant-based protein sources
When cooking with plant-based protein sources, it’s important to consider a few tips. Firstly, marinating tofu, tempeh, or seitan can enhance their flavor. Secondly, using spices, herbs, and sauces to season and add depth to plant-based proteins can make them more satisfying. Additionally, experimenting with different cooking techniques, like grilling, roasting, or sautéing, can bring out different textures and flavors. Lastly, incorporating plant-based proteins into a variety of dishes, such as stir-fries, stews, or casseroles, can help keep your meals interesting and flavorful.
Health Benefits of Plant-Based Protein
- Impact on heart health: Incorporating plant-based protein into your diet has been shown to have positive effects on heart health. Plant-based proteins, such as soy and peas, have been linked to lower cholesterol levels and a reduced risk of heart disease.
- Aiding in weight management: Plant-based proteins, especially those derived from legumes and nuts, can contribute to weight management. These proteins are typically lower in calories and saturated fat compared to animal-based proteins, making them a healthier choice for those looking to maintain or lose weight.
Incorporating plant-based protein into your diet can have numerous health benefits, including improved heart health and weight management. It’s a simple yet effective way to support your overall well-being.
Impact on heart health
Incorporating plant-based protein into your diet can have a positive impact on heart health. Plant-based proteins like soy and peas have been shown to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Plant-based protein can also aid in weight management. It is typically lower in calories and saturated fat compared to animal protein, making it a healthier option for those looking to lose weight. Additionally, plant-based proteins are high in fiber, which helps to promote feelings of fullness and prevent overeating. Including plant-based protein in your meals can support your weight loss goals and help you maintain a healthy weight.
Plant-Based Protein vs. Animal Protein

Nutritional differences:
- Plant-based proteins tend to be lower in calories and saturated fat compared to animal proteins, making them a healthier option for overall health.
- Plant-based proteins are high in fiber, which helps promote feelings of fullness and prevent overeating.
- Animal proteins, such as red meat, can be higher in cholesterol and may increase the risk of heart disease when consumed in large quantities.
Environmental and ethical considerations:
- Plant-based proteins have a lower environmental impact, as they require fewer resources and produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to animal-based protein sources.
- Choosing plant-based proteins can also align with ethical considerations, such as animal welfare and reducing animal exploitation.
Overall, incorporating more plant-based protein in your diet can provide numerous health benefits while also reducing your environmental footprint and supporting ethical choices.
Nutritional differences
Plant-based proteins offer several nutritional advantages compared to animal proteins. They tend to be lower in calories and saturated fat, making them a healthier option for overall health. Additionally, plant-based proteins are high in fiber, which promotes feelings of fullness and helps prevent overeating. On the other hand, animal proteins, such as red meat, can be higher in cholesterol and may increase the risk of heart disease when consumed in large quantities. Overall, incorporating plant-based protein into your diet can support a healthier lifestyle.
Environmental and ethical considerations
In addition to the nutritional benefits, incorporating plant-based protein into your diet also has positive environmental and ethical considerations. Plant-based proteins have a lower carbon footprint compared to animal proteins, as the production of meat and dairy products contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. Choosing plant-based protein also supports animal welfare, as it eliminates the need for the exploitation of animals in the food industry. By making this conscious choice, you can contribute to a more sustainable and compassionate food system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, incorporating plant-based protein into your diet can provide numerous health benefits, including improved heart health and weight management. It is also a sustainable and ethical choice, as it has a lower carbon footprint and supports animal welfare. To incorporate plant-based protein into your diet, try adding soy-based proteins, such as tofu or tempeh, and explore pea protein options. Experiment with plant-based protein meal ideas and consider cooking with these protein sources to enhance your overall nutrition and well-being.
Key takeaways on plant-based protein
Key Takeaways on Plant-Based Protein:
- Plant-based protein sources include soy, peas, and other legumes.
- Incorporating plant-based protein in your diet can improve heart health and aid in weight management.
- Soy-based proteins like tofu and tempeh provide complete amino acids.
- Pea protein is rich in essential amino acids and has additional benefits like supporting muscle growth and repair.
- Try plant-based protein meal ideas like chickpea curry or lentil burgers for variety.
- Cooking with plant-based protein sources can enhance your overall nutrition and well-being.
Resources for further information and recipes
Finding reliable resources and recipes can be a helpful way to incorporate more plant-based protein into your diet. Check out reputable websites, cookbooks, and social media pages dedicated to plant-based eating. Some popular resources include “The China Study” by T. Colin Campbell, “Oh She Glows” by Angela Liddon, and websites like Forks Over Knives and Minimalist Baker. These platforms offer a wide range of recipes and information on plant-based protein sources, cooking techniques, and meal planning. Exploring these resources will provide you with inspiration and knowledge to diversify your plant-based protein intake.
For More Blogs visit Aerns

